. Cost-effective optimization of rubble-mound breakwater cross sections. Breakwaters; Breakwaters. guidance available in the Shore Protection Manual (SPM) (1984) provides the basic tools for planning and designing breakwaters. This paper is intended to supplement that guidance by providing a practical perspective to the wide variety of environmental data now available to coastal engineers for rubble- mound breakwater design. Scope 2. A brief review is presented of past and present criteria development procedures, design techniques, and related practical considerations, followed by a more detai
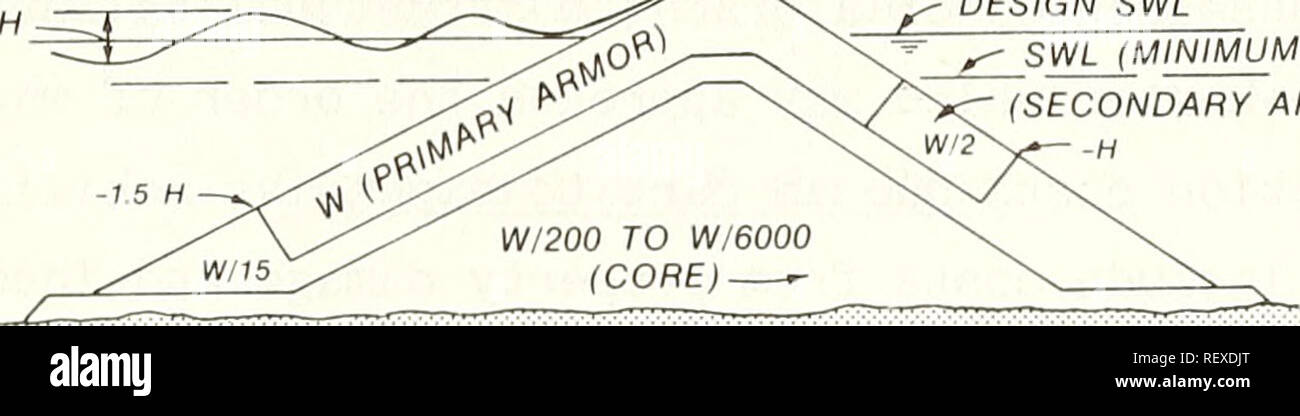
Image details
Contributor:
The Book Worm / Alamy Stock PhotoImage ID:
REXDJTFile size:
7.2 MB (191.4 KB Compressed download)Releases:
Model - no | Property - noDo I need a release?Dimensions:
3156 x 792 px | 26.7 x 6.7 cm | 10.5 x 2.6 inches | 300dpiMore information:
This image is a public domain image, which means either that copyright has expired in the image or the copyright holder has waived their copyright. Alamy charges you a fee for access to the high resolution copy of the image.
This image could have imperfections as it’s either historical or reportage.
. Cost-effective optimization of rubble-mound breakwater cross sections. Breakwaters; Breakwaters. guidance available in the Shore Protection Manual (SPM) (1984) provides the basic tools for planning and designing breakwaters. This paper is intended to supplement that guidance by providing a practical perspective to the wide variety of environmental data now available to coastal engineers for rubble- mound breakwater design. Scope 2. A brief review is presented of past and present criteria development procedures, design techniques, and related practical considerations, followed by a more detailed discussion of breakwater damage prediction and estimation of wave transmission characteristics. A systematic procedure is proposed to formulate alternative cross-section designs, evaluate their structural and functional effectiveness, and determine detailed dimensions which realize max- imum net incremental benefits. Definition and Purposes of Rubble-Mound Breakwaters 3. Breakwaters and, to some degree, jetties and groins are designed as barriers to sea waves, providing calmer water in their lees. Wave barriers can be constructed in many different ways, including vertical-sided concrete caissons, sheet-pile walls, wooden crib structures, and floating bodies. The oldest and most common type of wave barrier is the rubble-mound breakwater be- cause of its typical economy and constructibility in harsh coastal conditions. The long history of rubble-mound breakwaters has proven them quite reliable in a wide range of environments (Bruun 1985). A rubble-mound breakwater consists of sloped layers of stone or concrete shapes that are sized to withstand wave attack, excess settlement or loss of fill material, and to prevent scour, as shown in the typical cross section in Figure 2. Their inherent flexibility DESIGN WAVE HEIGHT, H CREST ELEVATION :^ ^ CREST WIDTH DESIGN SWL SWL (MINIMUM) (SECONDARY ARMOR). Figure 2. A typical rubble-mound breakwater cross section. Please note that these